Pure Rotation
Rotation about a fixed axis
Pure rotation occurs when a body rotates about a fixed non-moving axis. The following figure illustrates fixed-axis rotation.
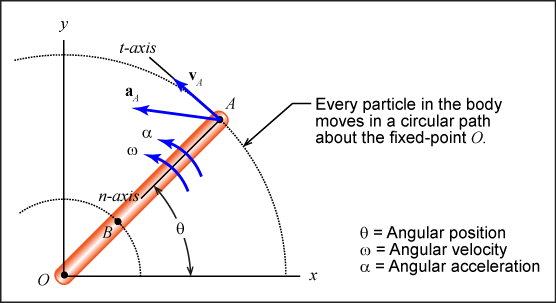
Motion characteristics
- Angular position: (θ) Angular position relative to an inertial coordinate axis. Similar to how θ was measured in polar coordinates.
- Angular velocity: (ω) How fast a body is rotating.
- Angular acceleration: (α) How fast a body's rotation rate is increasing or decreasing.
Angular kinematic relationships
- Angular velocity: The time rate of change of angular position. ω = dθ/dt
- Angular acceleration: The time rate of change of angular acceleration. α = dω/dt = d 2θ/dt 2
- Angular velocity / Angular acceleration: Combining the angular velocity and acceleration equations, we obtain α dθ = ω dω.
Angular motion parameter units
Angular motion direction
If the rigid body, shown in the above figure, is rotating in the counterclockwise direction, what direction is its angular velocity?
